Websites are made up of web pages under a domain name, where you browse content, use services, or shop online. You open amazon.com to buy products or visit google.com to find information.
Websites help you share information, connect with others, shop online, and find entertainment. If you run a business, a website makes your brand visible and helps you reach customers. If you’re an individual, you create a blog, portfolio, or personal website to showcase your work or ideas. E-commerce websites like Amazon let you shop from any location, and with millions of people buying online every day, they generate billions in sales.
Every website has key components. The domain name, like google.com, is the website’s address. Web hosting stores and delivers website files so users can access them. The frontend is what you see, like Google’s search bar. The backend processes requests and manages data. A database stores user logins and search history. Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress let you build and update websites without coding.
Websites serve different purposes. Static websites show the same content every time you visit, while dynamic websites update in real-time. If you shop online, you use an e-commerce website that handles payments and orders. Business websites help companies share information, and portfolio websites let professionals showcase their work. News websites keep you informed, while social networking sites help you connect and interact with others.
Building a website requires registering a domain name, selecting web hosting, and designing its layout. You can use coding languages or a Content Management System (CMS) like WordPress to develop it. SEO optimization improves search visibility, and security updates protect it from threats.
What is a Website?
A website is a bunch of web pages stored on a server that you can visit using a web browser. You get there by typing in a domain name. It’s a place online where you can see stuff like info, services, or even fun things to interact with.
Websites are used for sharing information, communication, business, shopping, and entertainment. Businesses use them to reach customers, sell products, and offer services. You can create a website for a blog, portfolio, or online community. Government and educational websites provide public resources and learning materials.
The benefits of websites include 24/7 accessibility, letting you find information or shop anytime. Businesses reach a global audience without physical locations. Websites improve communication through contact forms and live chat and build credibility by displaying reviews, testimonials, and professional content. According to the article “8 Essential Live Chat Statistics You Should Know in 2025,” published by Zoho SalesIQ on June 6, 2024, live chat has an overall customer satisfaction rating of 83.1%, outperforming traditional communication channels.
The first website, created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991, shared scientific information. Early websites were simple and text-based. By the late 1990s, design, multimedia, and e-commerce improved functionality. Today, websites support dynamic content, AI-driven features, and mobile-friendly experiences.
How Do Websites Work?
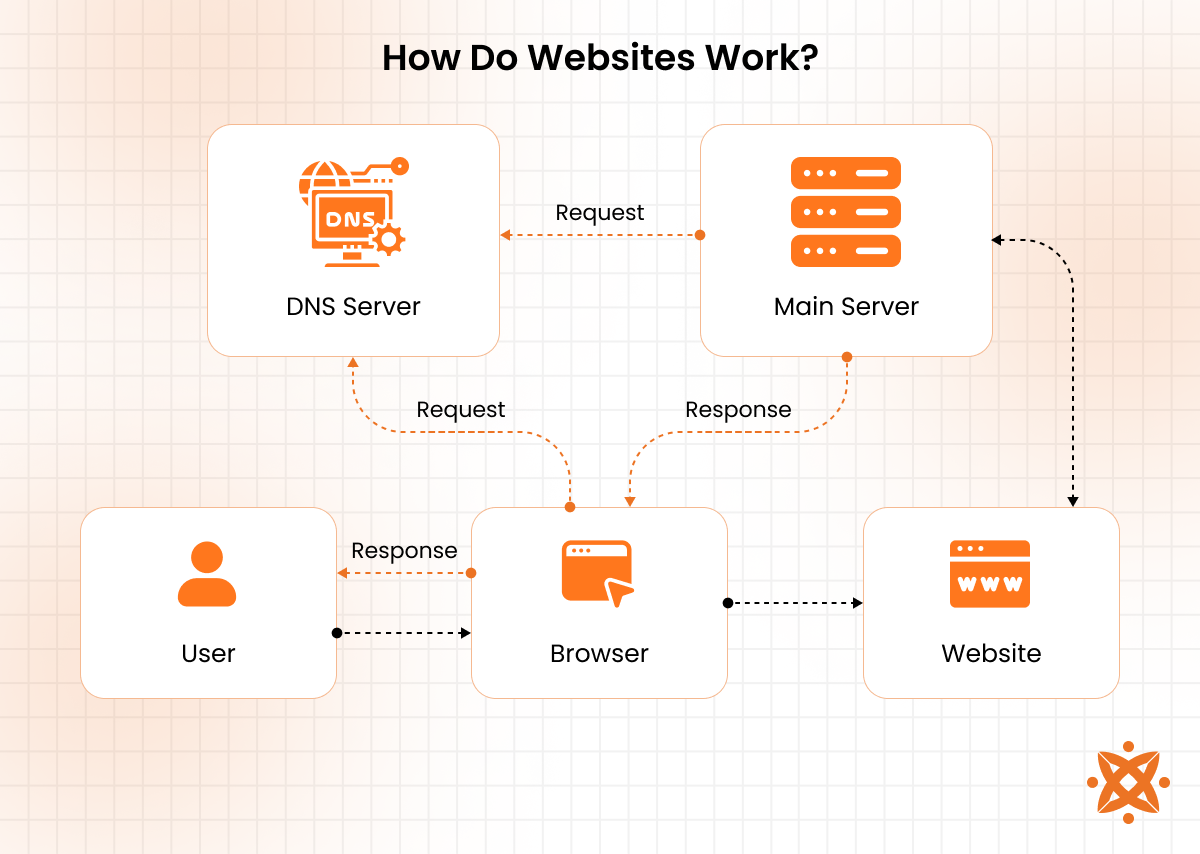
A website works by loading web pages when you enter a domain name in a browser. The browser contacts the Domain Name System (DNS) to find the website’s server by converting the domain name into an IP address.
Once the IP address is located, the browser sends an HTTP or HTTPS request to the server. The server processes the request and responds with website data, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
The browser reads the HTML structure, applies CSS for design, and executes JavaScript for interactive features. This process renders the webpage, allowing you to see and interact with the content.
Website performance depends on factors like server response time, page size, caching, and network speed. Faster servers, optimized images, and efficient coding improve loading speed, ensuring a smooth user experience. According to the article “10 Important Website Load Time & Speed Statistics of 2025,” published on Seomator Blog on January 12, 2025, clean, optimized coding aids faster web page loading by reducing unnecessary scripts, minifying CSS and JavaScript, and optimizing database queries.
What Are the Key Components of a Website?
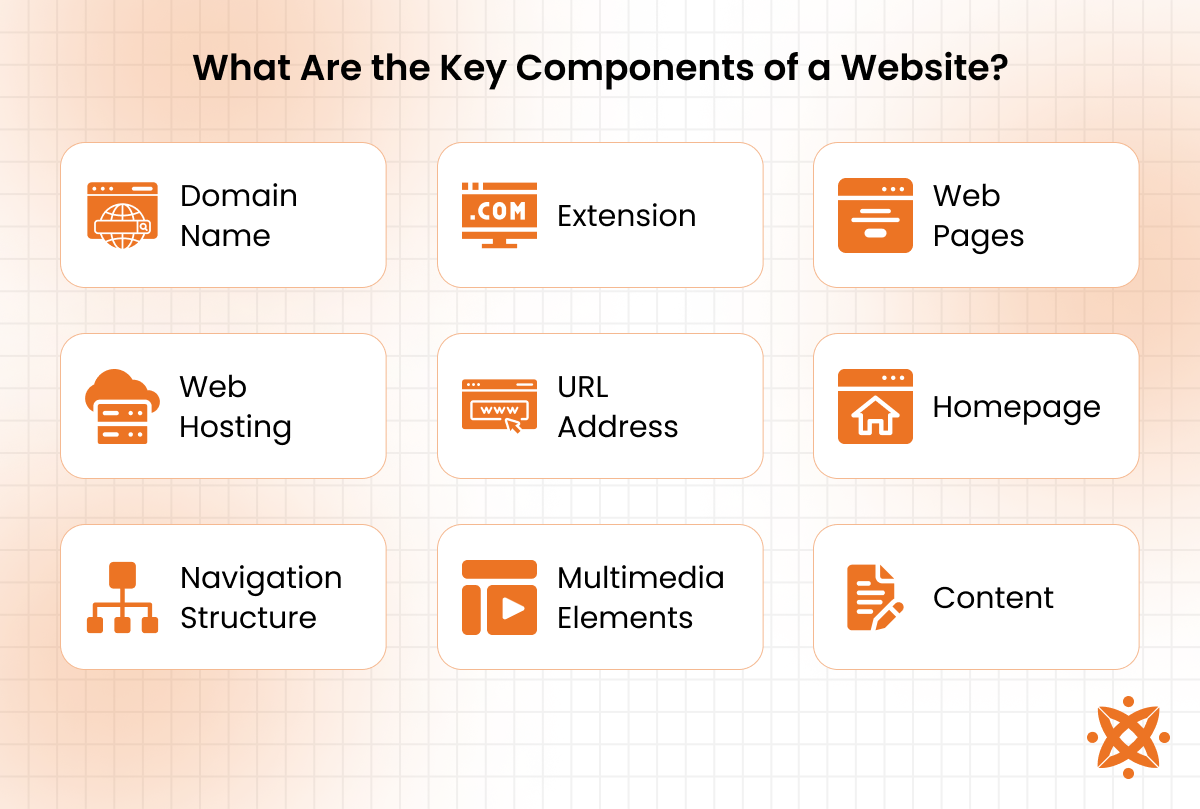
The major components of a website are domain name, web pages, web hosting, URL address, and navigation.
- Domain Name. A domain name is the website’s unique address, such as amazon.com. It allows users to access the website through a web browser. Without a domain name, users would need to enter an IP address to visit a website.
- Extension. A domain extension is the suffix attached to a domain name, such as .com, .org, .net, or .edu. It helps classify websites based on their purpose, with .com used for commercial sites and .org for organizations.
- Web Pages. Web pages are individual documents within a website that display content. They include homepages, product pages, contact pages, and blog posts. Each page is designed to serve a specific function and provide information to visitors.
- Web Hosting. Web hosting is the service that stores a website’s files and makes them accessible online. A hosting provider maintains servers that deliver web pages to users. Reliable hosting ensures fast loading speed, security, and minimal downtime.
- URL Address. A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the full web address of a page, such as amazon.com/products. It includes the protocol (HTTP/HTTPS), domain name, and specific page path, helping browsers locate website resources.
- Homepage. The homepage is the main entry point of a website. It provides an overview of the site’s content and directs users to different sections. A well-structured homepage improves navigation and user experience.
- Navigation Structure. Navigation structure includes menus, links, and buttons that guide users through a website. A clear navigation system helps visitors find information quickly, reducing bounce rates and improving usability.
- Multimedia Elements. Multimedia elements include images, videos, animations, and interactive features. These enhance engagement and improve communication by making content visually appealing and easier to understand.
- Content. Content is the text, images, and videos that convey information to users. Well-written content helps businesses communicate their message, improve SEO rankings, and keep visitors engaged.
What Are the Different Types of Websites?
The different types of websites are:
- Static Websites
- Dynamic Websites
- E-Commerce Websites
- Business Websites
- Portfolio Websites
- News Websites
- Social Media Websites
- Educational Websites
- Blogs
- Government Websites
Static Websites
A static website displays fixed content that does not change unless manually updated. It is built using HTML and CSS, making it simple and fast to load. These websites are ideal for personal portfolios, company profiles, and informational pages. Example: A small business website with basic contact details and services.
Dynamic Websites
A dynamic website generates content in real time based on user interactions. It uses programming languages like JavaScript, PHP, or Python to fetch and display data from a database. If you use Facebook or Netflix, you see different content based on your preferences. Example: Facebook and Netflix adapt content based on user preferences.
E-Commerce Websites
An e-commerce website lets you buy and sell products online. It includes shopping carts, payment gateways, and order management systems. These websites use security protocols to protect transactions. Example: Amazon and eBay facilitate millions of online purchases daily. The number of e-commerce websites has grown significantly, with Shopify alone hosting over 4 million stores, as reported in “E-commerce Growth Trends”, published by Statista on July 10, 2023.
Business Websites
A business website represents a company, helping you discover products, services, and contact details. Whether you’re looking for software development or consulting, businesses rely on websites to connect with customers. Example: Intelivita.com provides software development services.
Portfolio Websites
A portfolio website helps you showcase your work if you’re a designer, photographer, or writer. It highlights projects, testimonials, and contact details to attract clients. Example: A freelance graphic designer’s website displaying past work.
News Websites
A news website provides real-time updates on current events, politics, finance, and entertainment. These websites use multimedia elements like images and videos to engage readers. Example: BBC and CNN publish breaking news daily.
Social Media Websites
A social media website connects users, allowing them to share content, chat, and build networks. These websites use algorithms to suggest relevant content based on user behavior. Example: Instagram and Twitter enable global communication.
Educational Websites
An educational website offers courses, tutorials, and study materials. It includes interactive lessons, quizzes, and certification programs. Example: Coursera and Khan Academy provide online learning resources.
Blogs
A blog is an ongoing collection of articles, guides, and updates. Whether you follow tech trends or personal finance tips, blogs provide insights and opinions. Example: A tech blog covering app development trends.
Government Websites
A government website provides official information, services, and updates from public institutions. It includes tax filing portals, permit applications, and policy announcements. Example: USA.gov offers government-related resources and services.
How to Develop a Website
To develop a website, follow these steps:
- Choose a Domain Name.Pick a unique domain name that represents your website. Use an extension like .com, .org, or .net, depending on your purpose.
- Get Web Hosting.Select a hosting plan to store your website files and make your site accessible online. Choose shared, VPS, or dedicated hosting based on your traffic needs.
- Plan Your Website Structure.Outline the key pages you need, such as Home, About, Services, and Contact, to create a clear navigation flow. A well-structured site helps visitors find information easily.
- Design Your Website.Use a website builder, a CMS like WordPress, or custom code with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Make sure your design is responsive so it works on all devices.
- Develop Backend Functionality.If your website needs dynamic features like user logins or product databases, use PHP, Python, or Node.js to build the backend.
- Test Your Website.Check for broken links, slow loading speeds, and mobile responsiveness before launching. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to optimize performance.
- Launch and Maintain Your Website.Publish your website and monitor its performance. Regularly update your content, fix errors, and improve security to keep your site running smoothly.
Why Do You Need a Website?
You need a website to establish an online presence, build credibility, reach a wider audience, generate leads, sell products or services, and improve customer engagement.
- Establish an Online Presence. A website makes your business or personal brand visible to anyone searching online. It ensures that customers can find you easily.
- Build Credibility. A website provides professional information, testimonials, and case studies, helping customers trust your brand. Without one, your business may seem unreliable.
- Reach a Wider Audience. Unlike a physical store, a website allows you to connect with customers globally, increasing your potential market.
- Generate Leads. Contact forms, subscription sign-ups, and chatbots help capture visitor information, turning them into potential customers.
- Sell Products or Services. An e-commerce website lets you sell directly to customers, process payments, and automate transactions.
- Improve Customer Engagement. Websites integrate features like live chat, FAQs, and blogs, keeping users informed and interacting with your brand.
According to Statista, in the report “Global Website Usage Trends”, published on June 10, 2023, over 71% of small businesses now have a website, while 81% of consumers research online before making a purchase.
Consequences of Not Having a Website
Not having a website limits your ability to attract customers, build credibility, and grow your business. In a digital-first world, businesses without websites struggle to compete and miss valuable opportunities.
- No Online Presence. Customers can’t find you, reducing visibility and business growth.
- Loss of Credibility. Without a website, your business may seem outdated or untrustworthy, leading potential customers to choose competitors.
- Missed Sales & Leads. Without an e-commerce or lead generation system, businesses lose potential revenue from online shoppers.
- Limited Customer Engagement. A website provides tools like live chat and self-service options, making it easier for visitors to interact with your brand.
- Competitive Disadvantage. Competitors with websites attract more customers through SEO, online ads, and digital marketing, leaving businesses without websites behind.
What is the Difference Between a Website, Webpage, and Web Server?
The difference between a website, webpage, and web server is that a website is a collection of web pages, a webpage is a single document within a website, and a web server is the system that stores and delivers web pages to users.
A website consists of multiple interconnected webpages accessed through a domain name. It includes a homepage, about page, and other sections that provide information or services.
A webpage is an individual page within a website that displays text, images, videos, or interactive elements. Each webpage has a unique URL.
A web server is the physical or cloud-based system that stores website files and responds to user requests. When you enter a website’s URL, the web server retrieves the required webpage and displays it in your browser.
What is the Difference Between a Static and a Dynamic Website?
The difference between a static website and a dynamic website is that a static website displays the same content to every visitor, while a dynamic website updates content based on user interactions or database queries.
A static website is built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and stays the same unless manually updated. These websites load fast and use fewer server resources, making them ideal for portfolios, company profiles, and informational pages.
A dynamic website changes content in real-time based on user actions. It runs on server-side programming languages like PHP, Python, or JavaScript, pulling data from a database. Dynamic websites create personalized experiences, such as user dashboards, product recommendations, and interactive features.
What is the Difference Between a Website and a Web Application?
The difference between a website and a web application is that a website gives you information, while a web application lets you interact with data and perform tasks.
A website is a collection of static or dynamic pages that display content. It provides information but has limited interactive functionality
When you visit a website, you read content, browse pages, and maybe watch videos or view images. Websites can be static or dynamic, but they mostly provide information without requiring much user interaction.
A web application does more than just display content—it lets you log in, enter data, and complete tasks. It processes user input using backend programming and databases.