A bad website is one that fails to meet user needs and does not fulfill its purpose. It suffers from poor user experience, ineffective design, and technical shortcomings that frustrate visitors and hinder engagement. These issues not only deter users but also negatively impact a business’s credibility and conversion rates.
To avoid key pitfalls when designing or evaluating a website, it’s important to focus on user-centric design, ensure mobile responsiveness, optimize loading speeds, and provide clear calls to action. Additionally, selecting the right web development company plays a vital role in creating an effective website.
Factors to consider when choosing a web development company include project quality, communication, and long-term success. Evaluate the company’s technical expertise to ensure it aligns with your project scope and complexity. Look for a strong portfolio that reflects their design capabilities and industry experience.
According to Loopex Digital, titled “90+ important Web Design Statistics for 2025: Trends That Matter,” 2025, 88% of web users are less likely to return to a website after a poor user experience. Furthermore, businesses leave 35% of their money on the table due to a bad user experience.
What Are The Key Aspects Of A Bad Website?
The key aspects of a bad website are confusing navigation, non-responsive design, slow loading speed, low-quality content, lack of clear call-to-action (CTA), poor SEO practices, visual overload or outdated design, lack of accessibility, poor mobile experience, and weak security features.
Confusing Navigation
Confusing navigation refers to a website’s menu and link structure that hinders users from easily finding information. Poor navigation leads to frustration, increased bounce rates, and reduced user engagement. Effective navigation is vital for a positive user experience and retaining visitors.
Common causes of poor navigation include overloading menus with excessive options, which lead to decision paralysis. Unclear or jargon-filled labels confuse users about link destinations. Inconsistent navigation placement across pages disrupts user flow. Neglecting mobile-friendly design renders navigation unusable on smaller screens.
According to the Nielsen Norman Group titled “Usability Guidelines for Accessible Web Design,” 2024, websites with intuitive navigation structures increase user satisfaction by 135% and reduce task completion time by 50%.
To improve navigation, streamline menus by limiting top-level items to seven or fewer. Use clear, descriptive labels that reflect the content they link to. Maintain consistent navigation placement throughout the site. Implement a responsive design to ensure usability across devices.
Testing for user-friendly navigation involves several methods. Card sorting helps understand how users categorise information, informing the intuitive structure. Tree testing evaluates the findability of topics within the site’s hierarchy. Usability testing observes real users interacting with the site to identify navigation issues.
Non-Responsive Design
Non-responsive design refers to websites that do not adapt their layout and content to fit various screen sizes and devices. This results in a fixed display that appears distorted or requires excessive scrolling on smaller screens, leading to poor user experience and accessibility issues.
Technical issues contributing to non-responsiveness include fixed-width layouts that prevent content from adjusting fluidly to different screen dimensions. Additionally, using absolute units like pixels for element sizing restricts flexibility, and neglecting viewport meta tags causes improper scaling on mobile devices.
To achieve responsiveness, implement fluid grid layouts that use relative units such as percentages, allowing content to scale proportionally. Incorporate flexible images and media that resize within their containing elements, and apply CSS media queries to adjust styles based on device characteristics like width and orientation.
Testing for responsive design involves using tools like browser developer tools to simulate various screen sizes and devices. Additionally, online platforms such as Responsinator or BrowserStack enable testing across multiple devices and resolutions to ensure a consistent user experience.
According to Hostinger, titled “21 important Web Design Statistics for 2025,” 2025, 90% of websites have implemented responsive design, highlighting its widespread adoption and importance in modern web development.
Slow Loading Speed
Slow loading speed refers to the delay experienced when a website takes an extended time to display its content fully. This delay leads to user frustration and increased bounce rates. Web performance optimisation aims to enhance the speed at which web pages are downloaded and displayed, improving user satisfaction and retention.
Unoptimised images, excessive HTTP requests, bulky code, and JavaScript issues are common causes of slow load times. These factors hinder a website’s performance, leading to longer load times and decreased user engagement.
Important speed optimisation techniques involve compressing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, leveraging browser caching, and reducing server response times. Implementing these strategies leads to faster page loads and improved user experiences.
Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and Pingdom are utilised to measure and test loading speed. These tools analyse various performance metrics, providing insights into areas that require improvement.
According to a study by the Content Marketing Institute titled “Tools to Measure Website Load Time,” 2024, utilising tools like Google Speed Scorecard helps assess the impact of website speed on revenue, emphasising the importance of performance optimisation.
Low-Quality Content
Low-quality content refers to material that offers minimal value to readers and often lacks depth, originality, or relevance. Such content is characterised by thin information, excessive keyword stuffing, or duplication from other sources. Websites featuring low-quality content risk diminished credibility and reduced user engagement.
According to a study by The Ad Firm titled “How Thin Content Affects Your Website Performance,” 2023, websites with thin content experience higher bounce rates and decreased user engagement.
Content quality directly influences user engagement. High-quality content captivates readers, encouraging longer site visits and interactions. Conversely, low-quality content leads to increased bounce rates, as users quickly leave in search of more valuable information. Search engines monitor these behaviors, potentially lowering rankings for sites with poor engagement metrics.
To enhance content quality, focus on delivering comprehensive, original, and audience-centric material. Incorporate well-researched information, maintain clarity and coherence, and ensure the content aligns with user intent. Regularly updating content to reflect current trends and data also contributes to its value and relevance.
Measuring content quality involves analysing various engagement metrics. Key performance indicators include time spent on page, bounce rates, social shares, and conversion rates. Tools like Google Analytics provide insights into these metrics, aiding in the assessment and refinement of content strategies.
Lack Of Clear Call-To-Action (CTA)
A lack of clear calls-to-action (CTAs) on your website leaves visitors uncertain about their next steps, leading to missed opportunities for engagement and conversion. CTAs serve as signposts, guiding users toward desired actions such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or contacting your team. Without them, users navigate away without interacting further.
According to a study by Abmatic titled “The Importance of Having a Clear Call to Action on Your Website,” 2023, clear and effective CTAs are vital for guiding visitors and increasing conversions.
Issues arising from missing or unclear CTAs include decreased user engagement, lower conversion rates, and a lack of direction for visitors. Users feel lost or overwhelmed, unsure of how to proceed, which leads to frustration and site abandonment. This not only affects user experience but also impacts your site’s credibility and effectiveness.
To implement effective CTAs, ensure they are prominently placed, use compelling and action-oriented language, and are visually distinct to draw attention. For example, using phrases like “Get Started Today” or “Download Now” prompt immediate action. Additionally, aligning the CTA’s message with the user’s intent and the page’s content enhances relevance and effectiveness.
Testing CTA clarity and effectiveness involves A/B testing different versions to see which performs better. This could include variations in wording, color, placement, or design. Monitoring metrics such as click-through rates (CTR) and conversion rates provides insights into which CTAs resonate most with your audience.
Poor SEO Practices
Poor SEO practices encompass strategies that hinder a website’s visibility in search engine results. These include keyword stuffing, neglecting meta tags, and failing to optimise for mobile devices. Such practices lead to decreased traffic and lower search rankings.
Common SEO mistakes include ignoring keyword research, neglecting on-page optimisation, and overlooking mobile optimisation. These issues result in poor user experience and reduced search engine visibility. Addressing these mistakes is vital for improving site performance. As highlighted in a study by Yoast titled “6 common SEO mistakes and how to avoid them,” 2023, avoiding these pitfalls is vital for effective SEO.
To improve SEO, focus on conducting thorough keyword research, optimising meta tags, and ensuring mobile responsiveness. Implementing these strategies enhances user experience and boosts search engine rankings. Regularly updating content and building quality backlinks are also vital components of a robust SEO strategy. These practices align with the recommendations provided in Google Search Central’s “SEO Starter Guide.”
Testing SEO effectiveness involves using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor traffic and rankings. These platforms provide insights into user behavior and site performance, allowing for data-driven adjustments. Regular audits identify areas for improvement and track the impact of implemented changes.
Visual Overload Or Outdated Design
Visual overload occurs when a website presents excessive or disorganised visual elements, leading to user confusion and difficulty in processing information. This cluttered design overwhelms users, increasing cognitive load and detracting from the overall user experience.
According to a study by The Alien Design titled “Cognitive Load in UX Design: Impact on User Engagement & Usability,” 2025, overloaded interfaces with too many elements competing for attention overwhelm the user, increasing cognitive load.
Cluttered designs negatively impact user experience by making it challenging to focus on important content and navigate the site effectively. Users experience frustration, leading to increased bounce rates and decreased engagement. Simplifying the visual presentation helps users process information more efficiently and improves overall satisfaction.
To enhance visual clarity, implement design improvements such as using whitespace strategically to separate content, maintaining a consistent color scheme, and limiting the number of fonts and styles used. Organising information hierarchically with clear headings and subheadings guides users through the content seamlessly. These practices contribute to a more intuitive and aesthetically pleasing interface.
Assessing visual clarity and effectiveness involves usability testing and gathering user feedback to identify areas of confusion or distraction. Tools like A/B testing compare different design versions to determine which layout performs better in terms of user engagement and conversion rates. Regularly reviewing analytics data helps in making informed design decisions to optimise user experience.
Lack Of Accessibility
Lack of accessibility in web design refers to the failure to ensure that websites, tools, and technologies are usable by people with disabilities. This encompasses individuals with auditory, cognitive, neurological, physical, speech, and visual impairments. Inaccessible websites prevent users from perceiving, understanding, navigating, and interacting effectively with digital content.
Common accessibility issues include low-contrast text, missing alternative text for images, unlabeled form fields, and non-functional keyboard navigation. These barriers hinder the user experience for individuals relying on assistive technologies.
According to WebAIM titled “The WebAIM Million: An annual accessibility analysis of the top 1,000,000 home pages,” 2025, over 50 million distinct accessibility errors were detected across one million websites, averaging 51 errors per page.
To enhance accessibility, websites should implement features such as proper use of HTML semantic elements, alternative text for images, sufficient color contrast, and keyboard navigability. Adhering to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) ensures that content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users.
Testing for accessibility involves a combination of automated tools, manual evaluations, and user testing. Automated tools quickly identify common issues, while manual testing ensures that content is navigable and understandable. User testing with individuals who have disabilities provides valuable insights into real-world accessibility challenges.
Poor Mobile Experience
A poor mobile experience occurs when a website fails to function effectively on smartphones and tablets. Issues like slow loading times, unresponsive layouts, and difficult navigation frustrate users and lead to higher bounce rates. Ensuring a seamless mobile experience is vital for retaining visitors and achieving business goals.
Common issues with mobile design encompass unoptimised images that slow down page loading, navigation menus that are hard to use on smaller screens, and touch elements that are too small or too close together. Additionally, content that doesn’t adjust properly to different screen sizes makes reading and interaction challenging. These problems deter users from engaging with the site and completing desired actions.
To optimise for mobile, implement responsive design techniques that allow your website to adapt to various screen sizes. Compress images to reduce load times, simplify navigation for ease of use, and ensure buttons and links are appropriately sized for touch interaction. Regularly testing your site on multiple devices helps identify and address issues promptly.
Testing for mobile-friendliness involves using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test, which assesses how easily a visitor uses your page on a mobile device. Additionally, monitoring metrics such as mobile bounce rates and session durations provides insights into user experience. Addressing identified issues leads to improved engagement and conversion rates.
According to a study by Emarsys titled “Mobile Optimization: What It Is & How to Do It Successfully,” 2024, 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than three seconds to load.
Weak Security Features
Weak security features on a website refer to inadequate measures that fail to protect against unauthorised access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. This includes outdated software, a lack of encryption, poor password policies, and the absence of security protocols. Such vulnerabilities expose both the website and its users to potential risks.
Common risks associated with poor security include data theft, unauthorised access to sensitive information, and exploitation of vulnerabilities for malicious purposes. For instance, the absence of multifactor authentication (MFA) makes it easier for attackers to compromise user accounts.
Implementing important security measures is vital to safeguard your website. These include using SSL certificates to encrypt data transmission, regularly updating software and plugins to patch known vulnerabilities, enforcing strong password policies, and enabling MFA for user accounts. Additionally, conducting regular security audits and employing web application firewalls helps detect and prevent potential threats.
Testing the effectiveness of your website’s security involves several practices. Vulnerability scanning tools identify known security issues, while penetration testing simulates cyberattacks to uncover weaknesses. Monitoring website logs and setting up alerts for suspicious activities also aids in the early detection of breaches.
According to a study by HackerOne titled “9 Ways to Do Website Security Testing & Critical Best Practices,” 2024, combining automated tools with manual assessments provides a comprehensive approach to website security.
Mistakes To Avoid When Choosing A Website Development Company
When choosing a website development company, the mistakes to avoid are focusing solely on cost, neglecting to review portfolios and client feedback, overlooking communication and project management processes, choosing a company without post-launch support, and failing to define clear project requirements. These issues derail your website goals, affect your brand image, and result in lost time and budget.
A careful, informed approach helps ensure a productive collaboration and a successful outcome.
Mistakes to avoid when choosing a web development company are:
Focusing solely on cost: Prioritizing the cheapest option leads to subpar results. Low-cost providers lack the expertise or resources to deliver a high-quality website. Investing appropriately ensures better functionality and long-term value.
Neglecting to review portfolios and client feedback: Failing to examine a company’s previous work and client testimonials results in hiring a team that doesn’t align with your vision. Portfolios showcase design styles and capabilities, while reviews provide insights into reliability and professionalism. Thorough research helps in making an informed decision.
Overlooking communication and project management processes: Effective communication is vital for project success. A lack of clear communication channels lead to misunderstandings and unmet expectations. Ensure the company has established protocols for regular updates and feedback.
Choosing a company without post-launch support: Websites require ongoing maintenance and updates. Selecting a company that doesn’t offer post-launch support leaves you struggling with technical issues. Confirm that the provider provides comprehensive aftercare services.
Failing to define clear project requirements: Unclear objectives lead to scope creep and project delays. Without well-defined goals, the development team do not meet your expectations. Establish detailed specifications before commencing the project.
Avoiding these pitfalls increases the likelihood of a successful partnership with a website development company. If you’re seeking a reliable team to bring your vision to life, consider reaching out to Intelivita. Our expertise ensures your project is handled with professionalism and precision.
What Makes A Good Website?
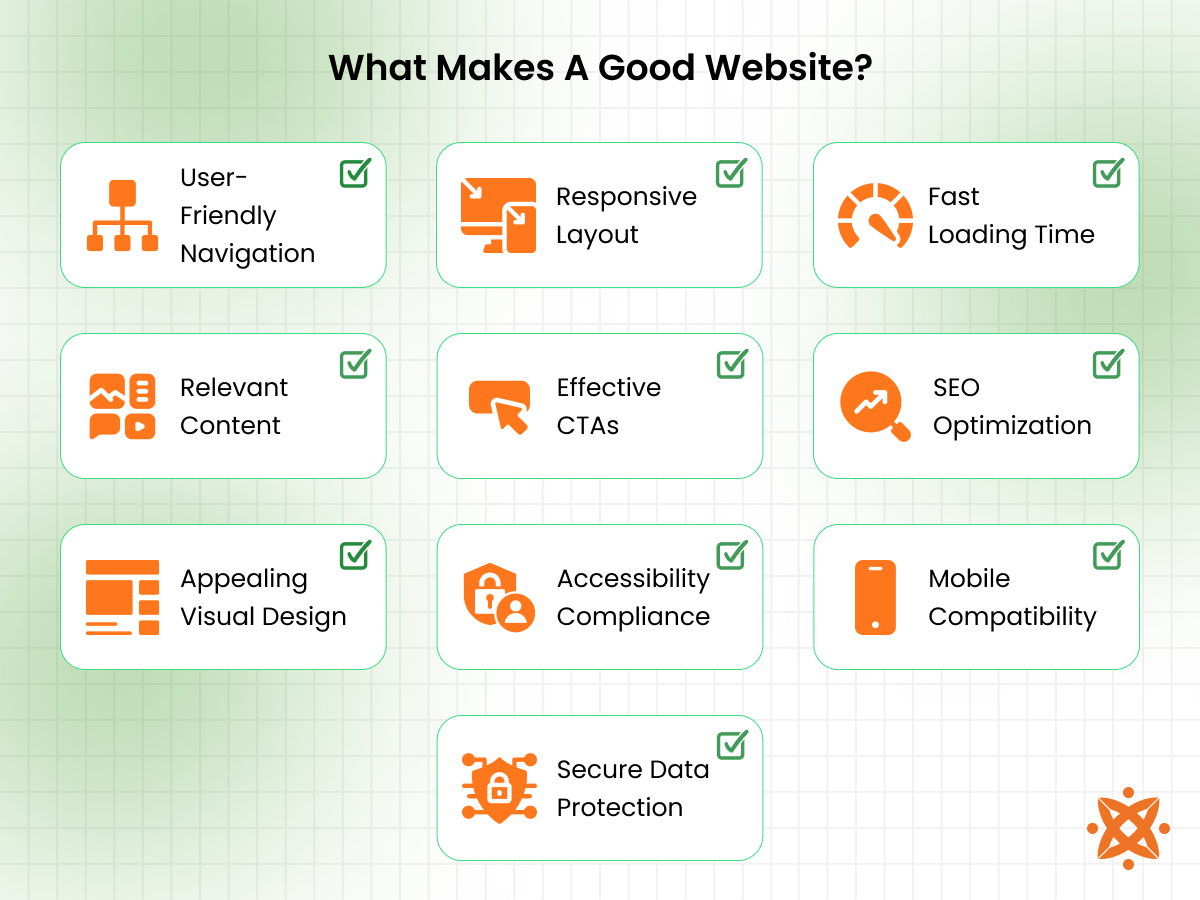
The key characteristics of a good website include user-friendly navigation, responsive layout, fast loading time, relevant content, effective CTAs, SEO optimisation, appealing visual design, accessibility compliance, mobile compatibility, and secure data protection. These elements work together to attract users, keep them engaged, and convert them into loyal customers.
A good website is known for features that support usability, trust, performance, and visibility.
The key characteristics of a good website are:
User-Friendly Navigation: The Navigation structure makes it easy for users to find information. Clear menus, intuitive labels, and consistent placement improve usability and reduce frustration.
Responsive Layout: Responsive design adapts to various screen sizes and devices. This ensures your website delivers a smooth experience across mobile, tablet, and desktop.
Fast Loading Time: Fast-loading pages improve user experience and reduce bounce rates. Optimising image sizes, reducing HTTP requests, and enabling caching are effective practices.
Relevant Content: Quality content speaks directly to user intent. It answers questions, builds authority, and encourages deeper interaction with your site.
Effective CTAs: Calls-to-action guide users to the next step. Clear language, strategic placement, and visual contrast boost engagement and conversions.
SEO Optimization: On-page SEO ensures visibility in search engines. Keyword integration, structured metadata, and crawlable content enhance ranking potential.
Appealing Visual Design: Aesthetic design creates positive impressions. Balanced colors, readable fonts, and white space contribute to visual clarity.
Accessibility Compliance: Accessible sites accommodate users with disabilities. Features like alt text, keyboard navigation, and ARIA labels support inclusivity.
Mobile Compatibility: Mobile-optimized websites improve performance on small screens. Responsive typography and touch-friendly elements enhance usability.
Secure Data Protection: Security builds trust with your users. SSL encryption, secure login, and regular audits protect data and deter threats.
A good website includes all these features to meet user needs and business goals. Focus on each one to create a platform that builds trust, encourages interaction, and supports growth.
How Much Does It Cost To Develop A Website?
The cost of developing a website ranges from $1,000 to $10,000, depending on factors such as complexity, features, and the development approach. For instance, a basic small business website costs less than $10,000, while a more complex, custom-built site with advanced functionalities exceeds $50,000. These estimates encompass expenses for design, development, content creation, and important integrations.
According to a study by Imaginovation titled “Website Development Cost in 2025: The Complete Guide,” 2025, the average cost of building a website often ranges from $1,000 (for a small business website) to $95,000 and more (for a complex custom website).
Ongoing maintenance and updates are additional costs to consider, ranging from $500 and $1,500 per year, depending on the website’s complexity and requirements. These recurring expenses cover hosting, security updates, content management, and technical support. Proper budgeting for both initial Website development costs and long-term maintenance is vital for sustaining an effective online presence.
How To Create A Business Website?
To create a business website, begin by identifying your goals and the type of experience you want to deliver to your visitors. Choose a domain name that reflects your brand identity and select a reliable hosting provider that offers strong uptime, fast loading speeds, and scalable features. Your website’s structure, design, and layout should follow a clear logic that aligns with your audience’s expectations.
According to a study by Investopedia titled “How to Start an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide,” 2023, testing and finalising a site before launch helps ensure your products and services are presented as intended and improves your chances of a successful launch.
Next, create content that resonates with your target audience. Focus on clarity, relevance, and value to keep visitors engaged. Make sure every page serves a specific purpose and supports your brand’s messaging. Optimise all content for search engines using well-researched keywords, proper meta descriptions, and structured internal linking to improve visibility on search platforms.
The final step is testing the site before launching. Review loading speed, mobile responsiveness, user navigation, and call-to-action effectiveness. Address all bugs or broken links, and check the site’s performance using analytics tools.
Can Poor Website Design Affect User Engagement And Business Goals?
Yes, poor website design negatively impacts user engagement and business goals. A cluttered layout, confusing navigation, and slow load times frustrate visitors, leading to higher bounce rates and reduced conversions.
According to a study by the University of California titled “A Literature Review: Website Design and User Engagement,” 2016, poorly designed websites frustrate users and result in a high “bounce rate,” or people visiting the entrance page without exploring other pages within the site.
On the other hand, a well-designed website with high usability has been found to positively influence visitor retention (revisit rates) and purchasing behavior. This highlights the importance of intuitive design in retaining users and achieving business objectives.
Furthermore, a site’s visual appeal and functionality play a pivotal role in shaping a user’s overall experience. A well-designed website not only captures attention but also retains it by making interactions seamless and intuitive. From the moment a visitor lands on a page, factors such as layout, color schemes, typography, and imagery come into play, creating either a sense of trust and professionalism or leading to confusion and disengagement.
A user-centric design focuses on clarity, simplicity, and responsiveness, ensuring that visitors easily interact with the content and navigate without unnecessary distractions. Elements such as load time, mobile-friendliness, and accessibility further enhance the SEO and user experience, contributing to longer sessions and higher engagement rates.
Conversely, cluttered or poorly optimised websites disrupt the user journey, resulting in frustration and higher bounce rates. Ultimately, website design is a powerful driver of user engagement, influencing not only how users perceive the brand but also their decision to explore further or convert.