The Android app development process involves programming languages such as Kotlin and Java, development tools such as Android Studio, and frameworks such as Flutter and React Native for cross-platform projects. Cross-platform frameworks enable developers to reuse code across Android and iOS, while Android Studio functions as the official IDE for coding, debugging, and testing Android applications. According to Statista’s 2025 report on Application Development Software, the market is projected to generate US$195.80 billion in revenue.
The best frameworks and tools for Android app development include Flutter, React Native, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic, and Titanium SDK. Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin support cross-platform development, while Cordova, Ionic, and Titanium SDK focus on hybrid app creation. These frameworks help developers reduce coding effort and accelerate Android application delivery.
The programming languages used for Android app development include Kotlin and Java for native apps, C++ and C# for performance-driven tasks, Dart for Flutter-based cross-platform apps, Python for AI-driven features, and JavaScript for hybrid frameworks. Kotlin is the preferred language for Android development, supported officially by Google since 2017. Its concise syntax, null safety, and interoperability with Java improve productivity. Java remains widely used because it provides stability and extensive libraries, including Android SDK packages for networking, database management, and UI development.
The process of developing an Android app includes planning and market research, UI/UX design, coding, testing and debugging, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. Developers use Android Studio to write and test code. After passing security scans and quality tests across devices and screen sizes, applications are published on the Google Play Store.
The main difference between Android and iOS app development lies in their operating systems, programming languages, and development environments. Android app development uses the Android operating system, relies on Kotlin and Java, and is built in Android Studio. In contrast, iOS app development is based on Apple’s iOS, uses Swift and Objective-C, and is developed in Xcode.
What Is Android App Development?
Android app development is the process of creating applications that run on the Android operating system. Android app development involves writing code, designing user interfaces, and integrating features such as authentication, push notifications, and secure data storage to create a fully functional application. Android development focuses on building apps that are optimized for performance, battery efficiency, and compatibility across Android devices including smartphones, tablets, wearables, and smart TVs.
According to StatCounter (2024), Android holds a global smartphone market share of over 70%, giving businesses the ability to reach the majority of mobile users worldwide through Android applications.
Use cases for Android apps include social media platforms like Instagram, e-commerce apps such as Amazon, productivity tools like Evernote and Trello, and games like PUBG Mobile. These apps serve various functions such as entertainment, online shopping, communication and education, showcasing the versatility and power of the Android platform.
What Is An Android App?
An Android app is an application designed to run on devices that use the Android operating system, such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. These apps are built using development tools such as Android Studio and programming languages like Kotlin or Java, ensuring responsive user interfaces, scalable performance, and seamless integration with Android APIs. Android applications range from simple utilities to complex enterprise systems, catering to diverse needs in entertainment, business, productivity, and communication.
The architecture of an Android app is layered, with the Linux-based Android OS managing processes, memory, and hardware. The Application Framework provides APIs such as location services, data storage, and notification management, while the Application Layer contains apps built with Java or Kotlin. Core components include Activities, Services, Broadcast Receivers, and Content Providers. Android’s open-source model allows customization and broad device support. Third-party integrations and Google services such as Maps, Drive, and the Play Store extend app functionality and increase user reach.
What Is The Definition Of Android?
The definition of Android is an open-source mobile operating system based on Linux, primarily used in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. Android was developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance (OHA), offering a flexible and customizable platform for app development and device interaction. Android has robust security features, including data encryption, app sandboxing, and secure app development frameworks.
Android provides developers with tools such as Android Studio and a large ecosystem of applications on the Play Store, making it one of the most popular operating systems globally. A key feature of Android is customizability, allowing users and developers to modify the interface and features according to their preferences.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop an Android Application?
The average app development cost for an Android application ranges from $10,000 to $18,000, depending on factors such as app complexity, feature set, UI/UX design, integrations, and team size. A basic Android app costs about $10,000, a moderate-complexity app around $12,000, and a complex app with advanced functionality about $18,000. A complex app with advanced functionality requires about $18,000. Development team location, hourly rates, and cross-platform support influence the total cost.
How Much Time Does It Take to Develop an Android Application?
Developing a simple Android app takes 1–3 months with a small team and limited features. A medium-scale app requires 4–6 months with additional integrations and more complex design. High-complexity apps such as marketplaces, gaming platforms, or enterprise solutions take 7 months or longer, depending on team size, frameworks, and backend requirements.
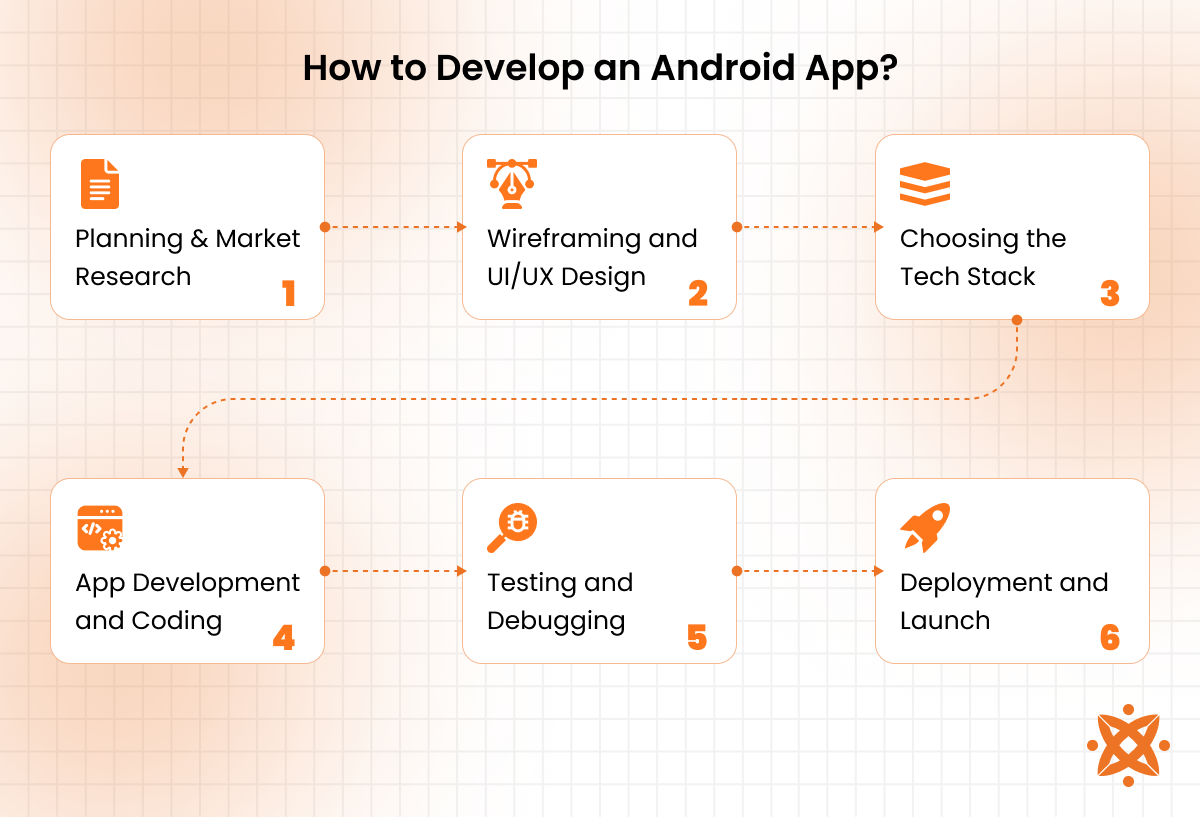
How to Develop an Android App?
The process of developing an Android app includes planning, designing, coding, testing, and deployment. These steps ensure a structured workflow, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
A 2014 study by Venkata N. Inukollu et al. on arXiv highlights that the mobile app development process involves several critical phases to ensure quality and success.
The processes to develop an Android app are explained below:
- Planning and Market Research: Planning involves defining the app’s purpose, target audience, and key features. Conducting market research helps identify user needs and competition. A clear roadmap ensures better execution and minimizes unnecessary revisions.
- Wireframing and UI/UX Design: Wireframing creates a visual blueprint of the app’s layout and functionality. UI/UX design ensures that the app is intuitive, aesthetically pleasing, and user-friendly. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD help streamline this process.
- Choosing the Tech Stack: Programming languages and frameworks directly affect app performance. Kotlin and Java are used for native Android apps, while Flutter and React Native are preferred for cross-platform development.
- App Development and Coding: This stage involves writing the app’s core logic and implementing UI components. Developers use Android Studio for coding, debugging, and testing. APIs, databases, and third-party integrations are incorporated to enhance functionality.
- Testing and Debugging: Testing ensures the app runs smoothly without crashes or bugs. Automated and manual testing identifies performance issues and security vulnerabilities. Tools like Espresso and Firebase Test Lab help streamline this phase.
- Deployment and Launch: Once tested, the app is prepared for release on the Google Play Store. This involves setting up a developer account, optimizing metadata (title, description, keywords), and adhering to the Play Store guidelines. Post-launch monitoring ensures improvements such as fixing bugs, adding new features, and optimizing performance based on user feedback.
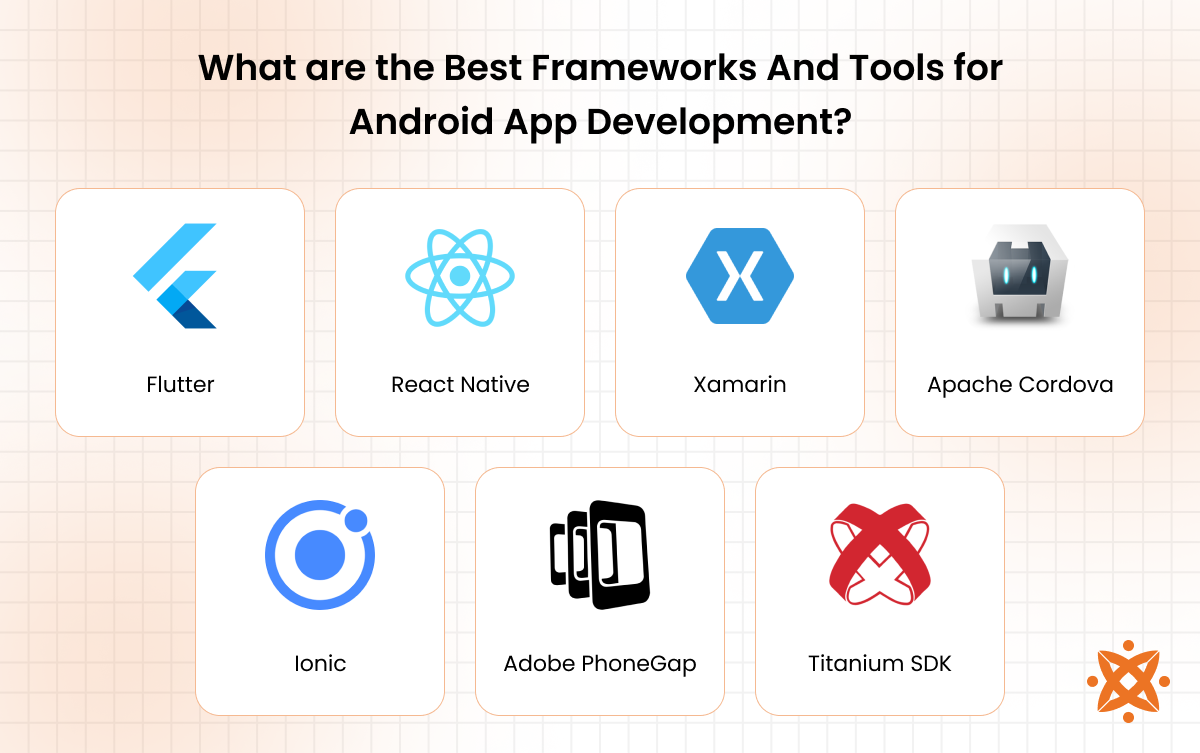
What are the Best Frameworks And Tools for Android App Development?
The best frameworks and tools for Android app development are Flutter, React Native, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic, Adobe PhoneGap, and Titanium SDK. These Android frameworks help developers build applications with varying capabilities: Flutter and React Native support near-native performance and scalability, Xamarin integrates with Microsoft’s ecosystem, while Cordova and Ionic enable simpler hybrid applications with payment, notification, and third-party integrations.
The best frameworks and tools for Android app development are as follows:
Flutter: Flutter is Google’s open-source UI framework for building cross-platform apps from a single codebase.
React Native: React Native, developed by Facebook, allows developers to build cross-platform mobile apps using JavaScript and React.
Xamarin: Xamarin is a Microsoft framework that uses C# and .NET to build cross-platform apps with native APIs.
Apache Cordova: Cordova enables hybrid apps built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, often used for simple utilities and business tools.
Ionic: Ionic is a UI toolkit that builds apps with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.
Adobe PhoneGap: PhoneGap, based on Apache Cordova, enabled hybrid apps using web technologies. Adobe discontinued it in 2020, and developers now use Cordova or Ionic as alternatives.
Titanium SDK: Titanium SDK allows developers to write apps in JavaScript that compile into native code.
How Does Android Studio Help in App Development?
Android Studio is Google’s official integrated development environment (IDE) for Android, providing tools for code editing, debugging, emulation, and performance analysis. Built on IntelliJ IDEA, it supports Kotlin, Java, and C++ as the primary languages for Android application development.
Android Studio provides built-in emulators, Gradle-based build automation, and a visual layout editor to help developers create, test, and optimize Android applications efficiently. Intelligent code suggestions, real-time error detection, and version control integration speed up coding and reduce bugs. Developers use Android Jetpack libraries and built-in templates to accelerate app development and reduce setup time.
What Is the Difference Between Native and Cross-Platform Android Frameworks?
The main difference between native and cross-platform Android frameworks is that native frameworks use platform-specific languages like Kotlin and Java for optimal performance, while cross-platform frameworks such as Flutter (Dart), React Native (JavaScript), and Xamarin (C#) allow code sharing across operating systems, reducing development time and cost.
Native frameworks offer better performance, full access to device capabilities, and seamless integration with Android APIs, while cross-platform frameworks focus on code reusability, faster development cycles, and lower costs but face UI inconsistencies compared to native apps.
Secondary differences include user experience and maintainability. Native apps provide a smoother user interface and optimized performance since they are built specifically for Android. In contrast, cross-platform apps, though efficient, face compatibility challenges and UI inconsistencies due to their generalized approach.
Native development requires separate codebases for iOS and Android, which increases development time and maintenance effort. Cross-platform frameworks enable single-codebase deployment, reducing costs and allowing faster updates across platforms.
What Programming Languages are Used for Android App Development?
The main programming languages used for Android app development are Kotlin, Java, C++, C#, Dart, Python, and JavaScript.
The main programming languages used for Android app development are as follows:
Kotlin: Kotlin is Google’s modern, concise language for Android. It offers null safety, minimal boilerplate, and seamless Java interoperability, which makes coding safer and faster. Kotlin compiles slower than Java and has a smaller ecosystem, but it is now the preferred choice for most new Android projects.
Java: Java is the long-standing foundation of Android development. It provides strong portability, libraries for networking and UI design, and backward compatibility, but its verbose syntax, higher memory use, and slower performance make it less efficient than Kotlin.
Dart: Dart powers Flutter and enables rapid, cross-platform UI development with hot reload and near-native performance. Its main limitations are a smaller ecosystem and limited adoption outside Flutter projects.
C++: C++ is used via the Android NDK for performance-intensive apps like games and multimedia. It offers speed and low-level control but requires complex coding, manual memory management, and has a steeper learning curve.
Python: Python is applied in Android projects involving AI, automation, or backend tasks through tools like Kivy and BeeWare. It is simple to learn and library-rich, but slower, memory-heavy, and less suited for native Android development.
Can You Develop an Android App With AI Like ChatGPT?
Yes, AI-powered tools such as ChatGPT can assist in Android app development by generating code snippets, debugging errors, automating test cases, and suggesting improvements, but they cannot completely replace human developers.
According to a 2019 report by NIST, AI technologies, including development tools like ChatGPT, support software engineering by improving reliability and creating more trustworthy systems.
Complex decision-making, custom logic, and performance optimization in Android apps require human expertise that AI tools cannot replace. AI tools such as GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini assist developers by suggesting real-time code completions, automating repetitive coding tasks, and detecting potential errors, but they do not eliminate the need for skilled developers.
What Is the Difference Between Android App Development and iOS App Development?
The main difference between Android app development and iOS app development is the operating system they are designed for. Android apps run on the Android OS, while iOS apps are built for Apple’s iOS.
Android development primarily uses Kotlin and Java in Android Studio, whereas iOS development relies on Swift and Objective-C in Apple’s Xcode IDE. Distribution differs significantly: Android apps are published through the Google Play Store with automated security checks, while iOS apps must pass Apple’s stricter App Store review process with manual approval.
Android apps support a wide range of device manufacturers, leading to fragmentation, whereas iOS apps are optimized for a limited number of Apple devices, ensuring better hardware-software integration. Android apps allow more customization and flexibility, while iOS apps emphasize security and a standardized user experience.
What Is the Difference Between Android App Development and Web Development?
The main difference between Android app development and web development is that Android apps run on mobile devices using the Android operating system. In contrast, web development focuses on building web applications that run in a browser. Android apps are developed using Kotlin, Java, or C++, whereas web applications use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Another key difference is deployment. Android apps must be installed from the Google Play Store or sideloaded, while web applications are accessed via a URL without installation. Android apps work offline by using local storage, whereas most web applications require an active internet connection to function. Android apps interact directly with device hardware such as GPS, cameras, and sensors, whereas traditional web applications have limited access to these features.
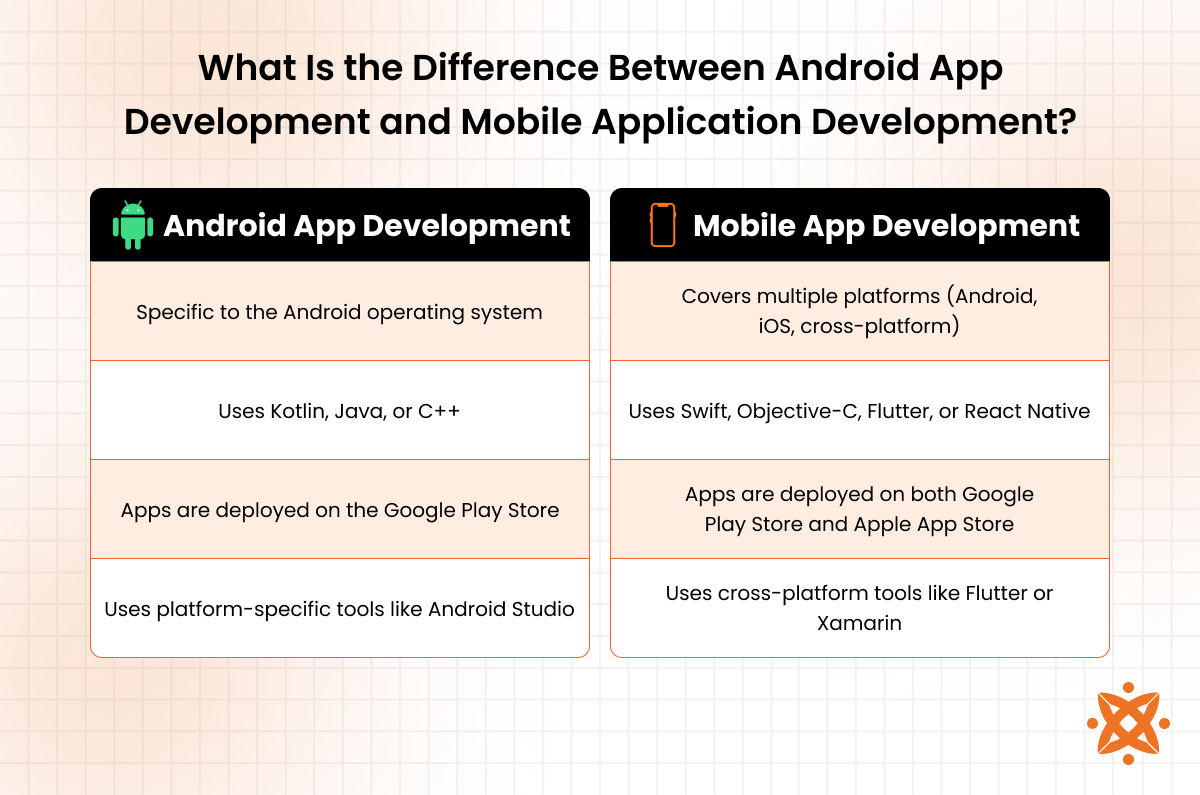
What Is the Difference Between Android App Development and Mobile Application Development?
The main difference between Android app development and mobile application development is that Android development is specific to the Android operating system, while mobile application development includes Android, iOS, and cross-platform applications.
Android apps are built using Kotlin, Java, or C++, while mobile app development uses Swift, Objective-C, Flutter, or React Native for broader compatibility. Android apps are distributed through the Google Play Store, while mobile apps are available on both Google Play and the Apple App Store.
Android development tools such as Android Studio are platform-specific, whereas mobile app development often relies on cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or Xamarin.
Can You Develop Android Applications on macOS?
Yes, Android applications can be developed on macOS. Android Studio, the official IDE, supports macOS and provides the full toolchain for coding, testing, and debugging.
Can You Develop Android Applications on Windows?
Yes, Android applications can be developed on Windows. Android Studio is fully compatible with Windows operating systems and offers the same development features available on other platforms.
Can You Develop Android Applications on Linux?
Yes, Android applications can be developed on Linux. Android Studio runs natively on Linux distributions and supports the complete Android development environment.
Do Android Development Tools Support Cross-OS Compatibility?
Yes, Android development tools support cross-OS compatibility. Android Studio is available for macOS, Windows, and Linux, ensuring developers can use the same IDE across different operating systems.
How To Choose the Right Android App Development Agency?
Choosing the right Android app development agency requires evaluating its portfolio of expertise, proficiency in Kotlin, Java, and cross-platform frameworks, UI/UX design capabilities, and the ability to provide long-term post-launch support. A reliable agency ensures quality, security, and long-term success.
The following criteria help in selecting the right Android app development agency:
- Expertise and Experience: An Android app development agency with a diverse portfolio demonstrates the ability to build robust applications. Reviewing past projects highlights their technical skills, while experience across multiple industries indicates adaptability.
- Technical Proficiency: Proficiency in Kotlin, Java, Flutter, and React Native ensures that an agency meets various app requirements. Advanced knowledge of APIs, databases, and cloud integration is important. Strong backend capabilities improve app performance.
- UI/UX Design Capabilities: A well-designed app enhances user engagement and retention. Agencies with a focus on intuitive design and smooth navigation create better user experiences. Reviewing past UI/UX projects helps assess their approach.
- Post-Launch Support: Regular updates, bug fixes, and maintenance keep an app functional and secure. A reliable agency provides long-term support to ensure compatibility with new Android versions and to resolve performance issues as they arise.
- Client Reviews and Case Studies: Testimonials and case studies provide insights into an agency’s reliability and success rate. Positive feedback from clients indicates trustworthiness, and a strong track record reflects consistent project delivery.
- Security and Compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations ensures app security. Agencies that follow best practices for encryption and secure coding minimize vulnerabilities. Compliance with industry standards prevents legal risks.
Choosing the right Android app development agency ensures a high-quality product and seamless user experience. Intelivita Android app development agency brings expertise in native and cross-platform Android development, ensures compliance with industry standards, and provides post-launch support to maintain long-term app performance.
What Is Android OS?
Android OS provides an adaptable and user-friendly environment for application development, offering seamless integration with Google services and third-party applications. It provides an adaptable and user-friendly environment for application development and offers seamless integration with Google services and third-party applications.
The characteristics of the Android OS include its open-source architecture, which allows developers to modify and optimize the system for different devices. Android OS supports multi-user profiles and multitasking capabilities, enabling smooth operation of multiple applications simultaneously for greater user flexibility. Android receives regular version updates from Google, enhancing security, performance, and functionality with annual major releases and monthly security patches.
Android OS is highly scalable, ensuring compatibility with hardware ranging from entry-level smartphones to flagship models. Android OS incorporates cloud integration, enabling synchronization with Google Drive, Photos, Gmail, and other cloud services, ensuring data accessibility across devices.
How Do Android Apps Make Money?
Android apps make money through in-app advertisements, in-app purchases, subscriptions, affiliate marketing, and paid apps. Advertisements use networks like Google AdMob for revenue from impressions or engagement. In-app purchases and subscriptions generate income from features, content, or services. Affiliate marketing provides commission through referrals, while paid apps charge users upfront. Many Android apps combine these models to maximize revenue.